40 label a transverse wave
Transverse wave - Wikipedia In physics, a transverse wave is a wave whose oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of the wave's advance. This is in contrast to a longitudinal wave which travels in the direction of its oscillations. Water waves are an example of transverse wave. A simple example is given by the waves that can be created on a horizontal length of ... Label & Draw Transersve Waves: Amplitude, Frequency ... - YouTube Learn how to QUICKLY label a transverse wave with crest, trough, wavelength, frequency, amplitude, resting position and resting points. We will also learn how to draw a transerve wave correctly...
Longitudinal Waves and Labelling wave diagrams - YouTube Longitudinal Waves and Labelling wave diagrams The Animated Teacher 15.6K subscribers Subscribe 5.7K views 2 years ago Tutorial video on longitudinal waves, examples of these waves and how to...
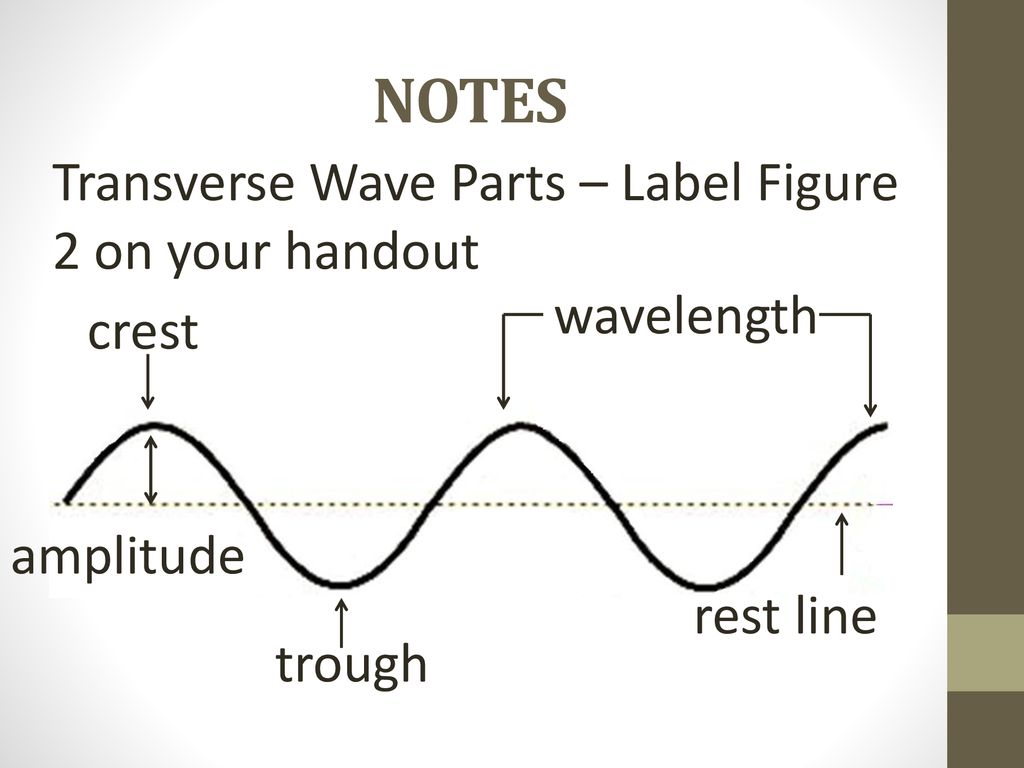
Label a transverse wave
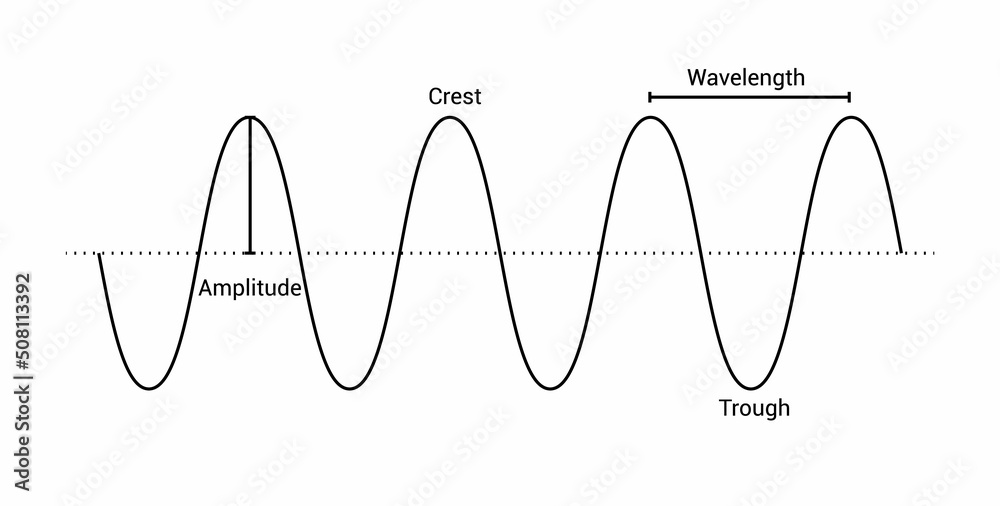
Label Parts of Waves - Labelled diagram - wordwall.net Label Parts of Waves - Labelled diagram Home Features Price Plans Log In Sign Up Language Crest, Trough, Wavelength, Amplitude, Rarefaction, Compression, Longitudinal, Transverse, Sound Wave, Electromagnetic Wave. Label Parts of Waves Share by Elizabetheck G6 G7 G8 Science Like Edit Content More Leaderboard Options Switch template Interactives What Are the Parts of a Transverse Wave? - Reference.com A transverse wave is one in which the energy of the wave displaces particles perpendicular to the energy wave. For instance, a ripple on a pond moves the water up and down, while the energy moves horizontally across the water. Springs moving up and down and vibrating piano strings are also physical examples of transverse waves. ADVERTISEMENT Label the parts of the transverse wave. Amplitude: - Brainly.com A transverse wave occillates perpenticular to the direction of energy transfer. A = Crest, B = trough, C = Amplitude, and D = Wavelength. Transverse Wave, In this wave oscillates perpendicular to the energy transfer. For example, Electromagnetic wave. Amplitude is the height of the wave from its mean point. Crest is the highest point of the wave.
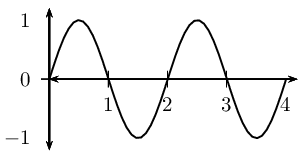
Label a transverse wave. 1.1: Transverse and Longitudinal Waves - Physics LibreTexts Figure 1.1: Example of displacements in transverse and longitudinal waves. The wave motion is to the right as indicated by the large arrows. The small arrows indicate the displacements at a particular instant. ... (kxx + kyy + kzz ). \label{2.9}\] Since wave fronts are lines or surfaces of constant phase, the equation defining a wave front is ... Wave characteristics review (article) | Khan Academy Distance between adjacent maxima or minima of a wave. Periodic wave: Wave that repeats over time and space. Also called a continuous wave. Crest: Highest point on a transverse wave. Also called the peak. Trough: Lowest point on a transverse wave. Expansion: A point of maximum spacing between particles of a medium for longitudinal waves. Compression Study Guide for Waves Test Flashcards | Quizlet Draw and label a longitudinal wave. Include compression, rarefaction and wavelength Give examples of the waves drawn in #1 and #2. Examples of a transverse wave are water waves and light waves and examples of a longitude wave are sound waves and a slinky being pushed back and forth (a pulse) and they move in the direction of the compression Transverse and longitudinal waves review - Khan Academy How to identify types of waves In a transverse wave, the particles are displaced perpendicular to the direction the wave travels. Examples of transverse waves include vibrations on a string and ripples on the surface of water. We can make a horizontal transverse wave by moving the slinky vertically up and down.
Examples, Speed & Reflection of a Transverse Waves - BYJUS A transverse wave is a wave in which particles move perpendicular to the direction of the wave propagation. A longitudinal wave is a wave in which the particles move in a direction parallel to the wave propagation. In this article, our focus will be on transverse waves and their characteristics. Speed of a transverse wave and and Important FAQs - VEDANTU The characteristics of transverse waves are: Transverse waves can only pass through solids and cannot pass through liquids or gasses. Polarization is a phenomenon that can only be observed in transverse waves. The plane of vibration, also known as polarization, is where all the particles in a medium vibrate at the same place. What does a diagram of a transverse wave indicate? - Quora A transverse wave is a wave in which the motion of the medium is sideways to the motion of the wave. This is like a wave on a clothesline. The rope moves sideways as the wave moves along the rope. In contrast, a wave moving along a Slinky toy is a longitudinal wave. Transverse vs. Longitudinal Waves | Characteristics, Diagrams ... Transverse waves are waves that are usually thought of when the term "wave" is used. The transverse wave definition is a wave in which the motion of the particles moves at right angles to the ...
Transverse waves - Waves - AQA Synergy - BBC Bitesize Transverse waves are often demonstrated by moving a rope rapidly up and down. In the diagram the rope moves up and down, producing peaks and troughs. Energy is transferred from left to right.... Label a transverse wave Diagram | Quizlet Label a transverse wave + − Flashcards Learn Test Match Created by Jennifer_Boyes Terms in this set (4) Wavelength the distance from one point on a transverse wave to an identical point on a second wave. The shorter the wavelength the higher the frequency of the wave Peak The highest point of a wave trough the lowest point of a wave Amplitude 16.2: Traveling Waves - Physics LibreTexts Waves may be transverse, longitudinal, or a combination of the two. Examples of transverse waves are the waves on stringed instruments or surface waves on water, such as ripples moving on a pond. Sound waves in air and water are longitudinal. With sound waves, the disturbances are periodic variations in pressure that are transmitted in fluids. Transverse & Longitudinal Waves Definition & Examples - BYJUS Transverse Waves And Longitudinal Waves In Physics, waves are explained as an oscillation about the fixed point, accompanied by the transfer of energy travelling from one medium to another. When energy transfer occurs through a medium due to oscillation, the resultant wave can be termed a mechanical wave.
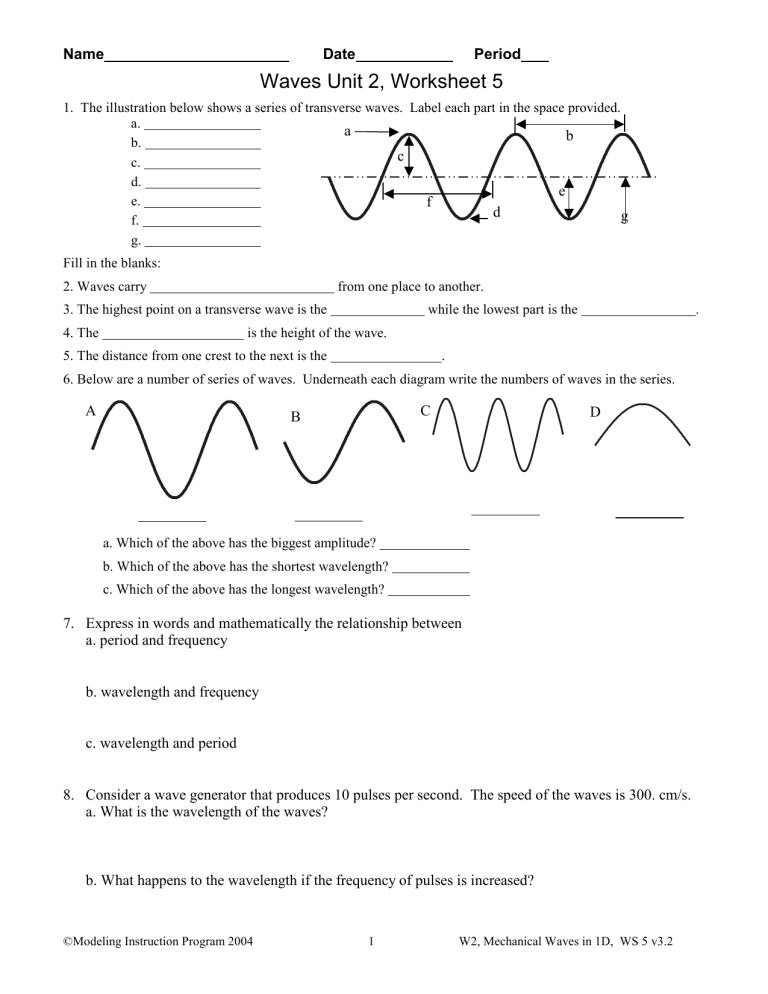
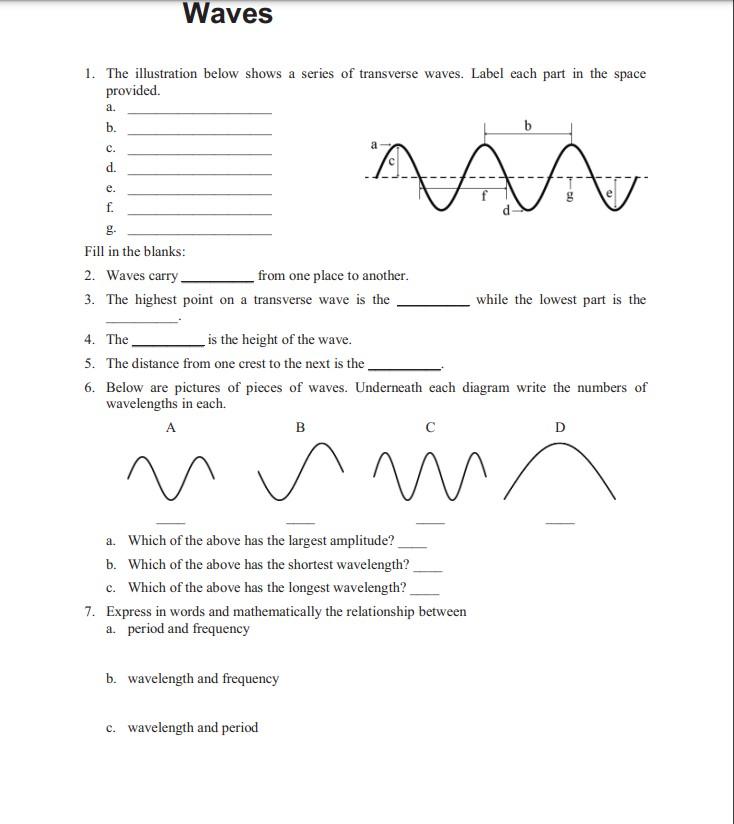
DOC Worksheet - Labeling Waves WORKSHEET - LABELING WAVES Study Guide WAVES 1. The highest point on a wave is the __ CREST __, while the lowest point is the __TROUGH___. 2. The _AMPLITUDE___ of a wave is a measure of the amount of energy it carries. 3. The distance from one point on a wave to the identical point on the next wave (crest to crest, etc. __WAVELENGTH_. 4.
Transverse Waves Teaching Resources | TPT - TeachersPayTeachers Waves Lab--Includes Transverse and Longitudinal Waves Exploration by Shafer's Science Store 4.9 (80) $3.99 PDF This lab is designed to serve as an introduction to a waves unit. Following the 5e inquiry-based instructional approach, students are exploring the concepts of waves prior to explicit instruction.
Label Parts Of A Wave Teaching Resources | Teachers Pay Teachers Wave Practice - Transverse Wave Label and Draw by Geo-Earth Sciences 4.9 (50) $1.50 PDF Wave Practice - Transverse Wave Label and Draw Review/Reinforcement/Practice Activity for students to define parts of a transverse wave and illustrate waves using standard measurements. Great practice activity or test review exercise.
Longitudinal and transverse waves - Properties of waves - Edexcel ... Transverse waves are often demonstrated by moving a rope rapidly up and down. In the diagram the rope moves up and down, producing peaks and troughs. Energy is transferred from left to right....
Transverse wave | Definition, Characteristics, Examples, Diagram ... transverse wave, motion in which all points on a wave oscillate along paths at right angles to the direction of the wave's advance. Surface ripples on water, seismic S (secondary) waves, and electromagnetic ( e.g., radio and light) waves are examples of transverse waves.
Dart Wiring: TransverseWave Learn how to quickly label a transverse wave with crest, trough, wavelength, frequency, amplitude, resting position and resting points. We will also learn how to draw a transerve wave. A diagram to show the inner structure of the ear the ear is made up of three different sections that work together: The outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear.
PDF WORKSHEET - LABELING WAVES - Physical Science Waves and Wave Properties Lesson—Anatomy of a Wave Worksheet WORKSHEET - LABELING WAVES 1. The highest point on a wave is the _____, while the lowest point is the _____. 2. The _____ of a wave is a measure of the amount of energy it carries. 3. The distance from one crest to the next crest is the _____. 4.
Label Parts of Waves - Labelled diagram - Wordwall Crest, Trough, Wavelength, Amplitude, Longitudinal, Transverse, Sound Wave, Water Waves, Wave at rest.
Physics Tutorial: The Anatomy of a Wave - Physics Classroom A transverse wave is a wave in which the particles of the medium are displaced in a direction perpendicular to the direction of energy transport. A transverse wave can be created in a rope if the rope is stretched out horizontally and the end is vibrated back-and-forth in a vertical direction.
PDF Transverse Waves - Paulding County School District Transverse Waves: Practice II Name_____ Instructions: Use the wave skeleton boxes below to create sine waves that match the characteristic measurements. Wave 1- Amplitude 1.5 inch Wavelength 2.5 inch (3 complete waves) Wave 2- Amplitude 1 inch Wavelength 1.25 inch (6 complete waves)
transverse wave diagram labeled - Chicise You create a transverse wave by inducing in the particles that make up a respective. In Physics, A Transverse Wave Is A Wave Whose Oscillations Are Perpendicular To The Direction Of The Wave's Advance. Learn how to quickly label a transverse wave with crest, trough, wavelength, frequency, amplitude, resting position and resting points.
Label the parts of the transverse wave. Amplitude: - Brainly.com A transverse wave occillates perpenticular to the direction of energy transfer. A = Crest, B = trough, C = Amplitude, and D = Wavelength. Transverse Wave, In this wave oscillates perpendicular to the energy transfer. For example, Electromagnetic wave. Amplitude is the height of the wave from its mean point. Crest is the highest point of the wave.
What Are the Parts of a Transverse Wave? - Reference.com A transverse wave is one in which the energy of the wave displaces particles perpendicular to the energy wave. For instance, a ripple on a pond moves the water up and down, while the energy moves horizontally across the water. Springs moving up and down and vibrating piano strings are also physical examples of transverse waves. ADVERTISEMENT
Label Parts of Waves - Labelled diagram - wordwall.net Label Parts of Waves - Labelled diagram Home Features Price Plans Log In Sign Up Language Crest, Trough, Wavelength, Amplitude, Rarefaction, Compression, Longitudinal, Transverse, Sound Wave, Electromagnetic Wave. Label Parts of Waves Share by Elizabetheck G6 G7 G8 Science Like Edit Content More Leaderboard Options Switch template Interactives
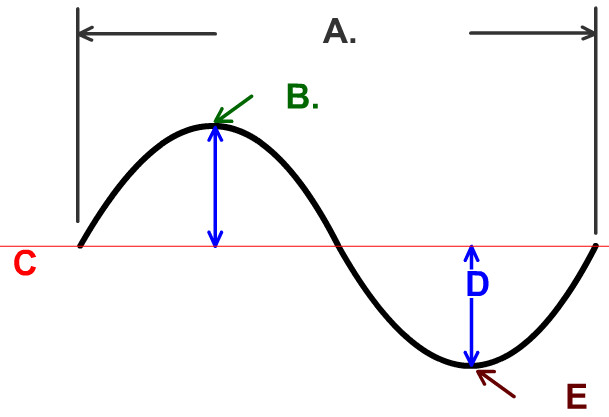
















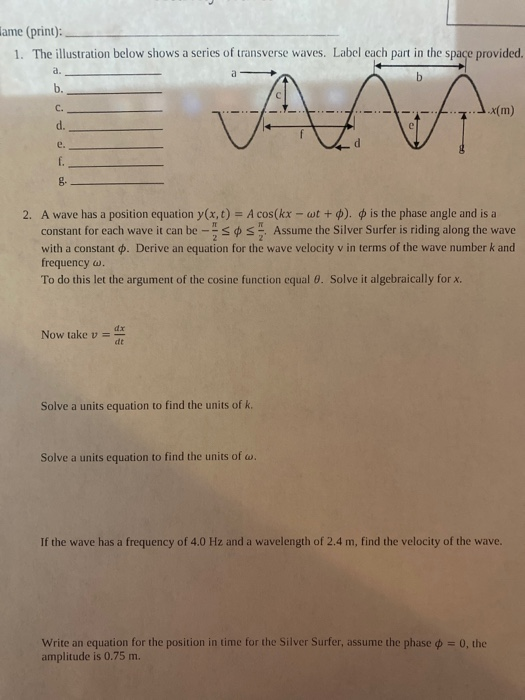









Post a Comment for "40 label a transverse wave"