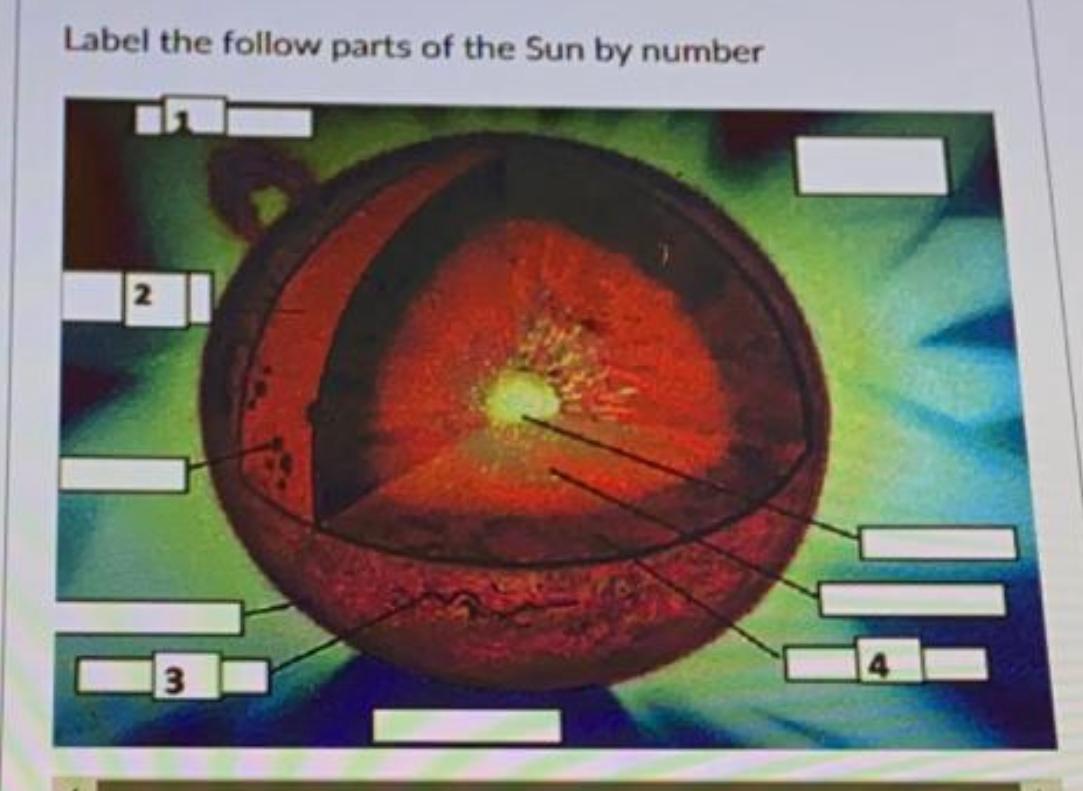
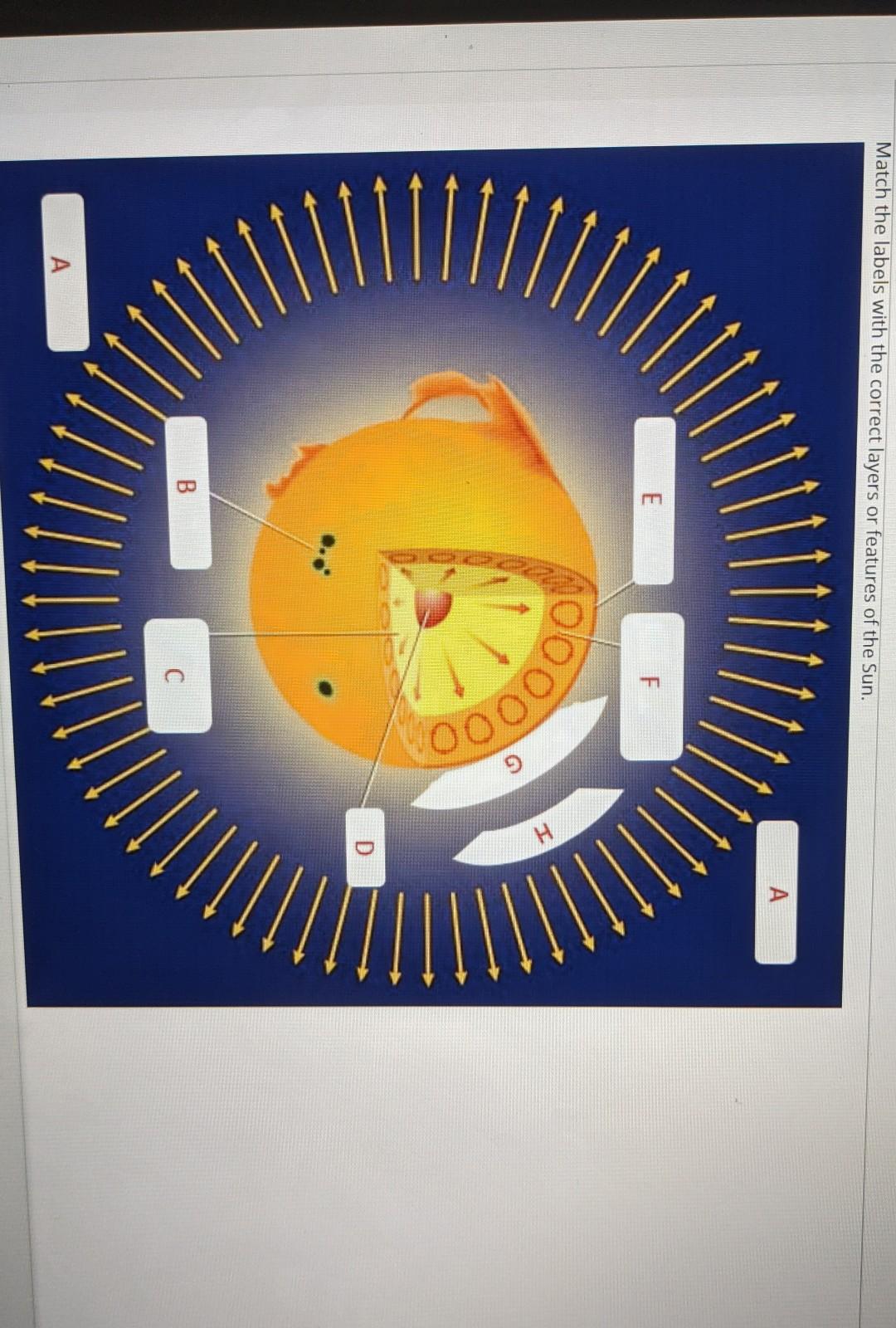
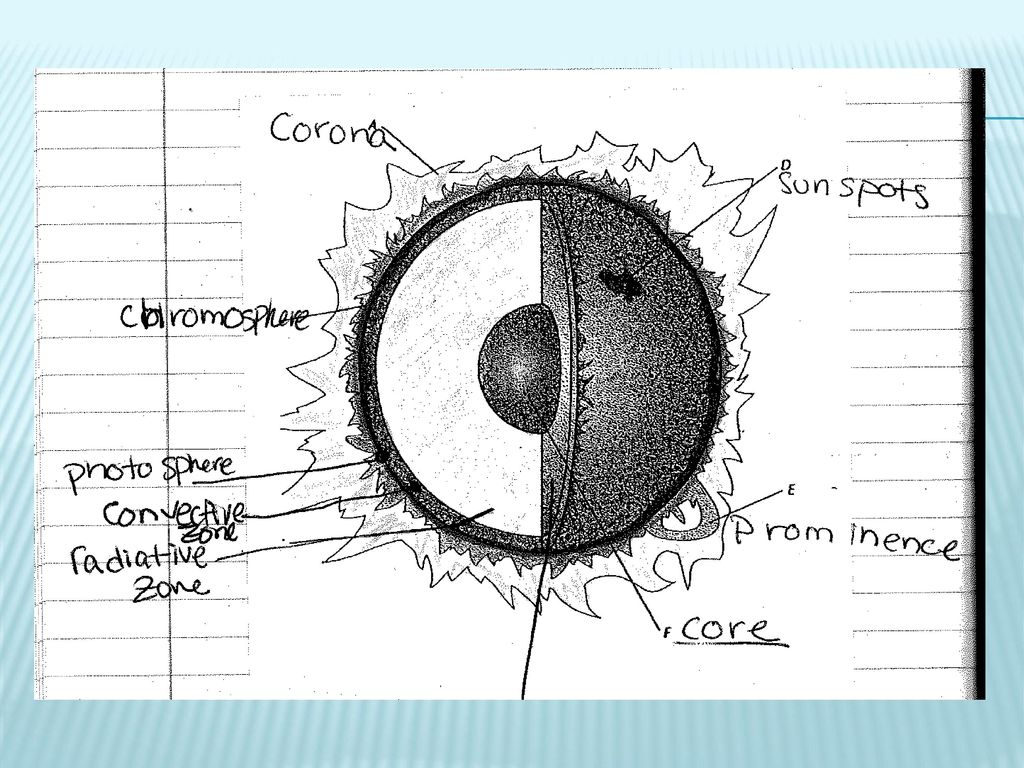
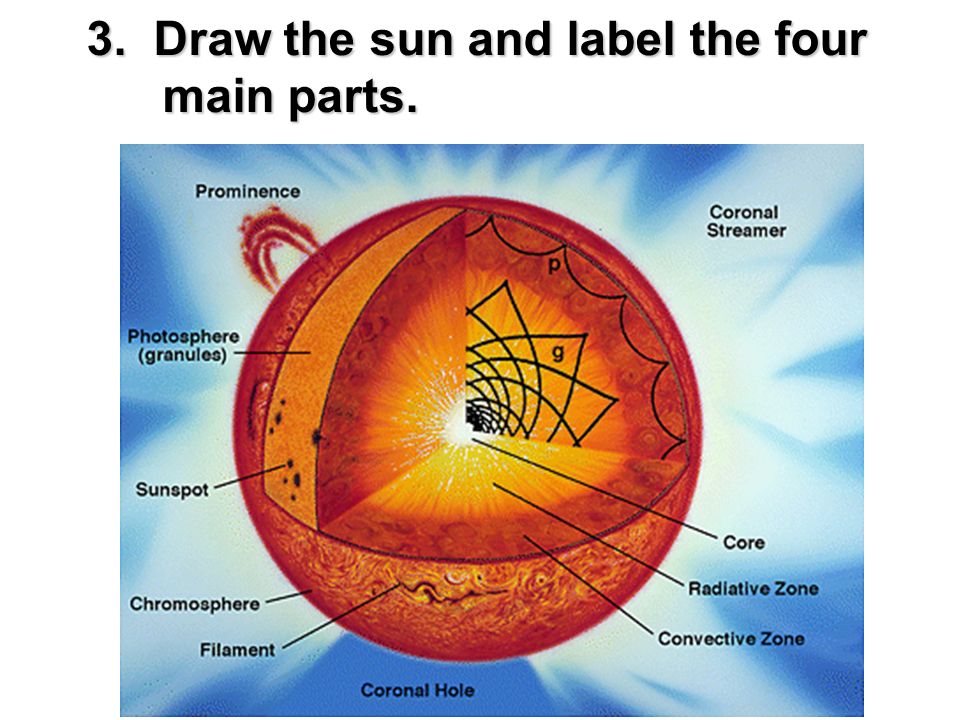
40 label the different areas of the sun.
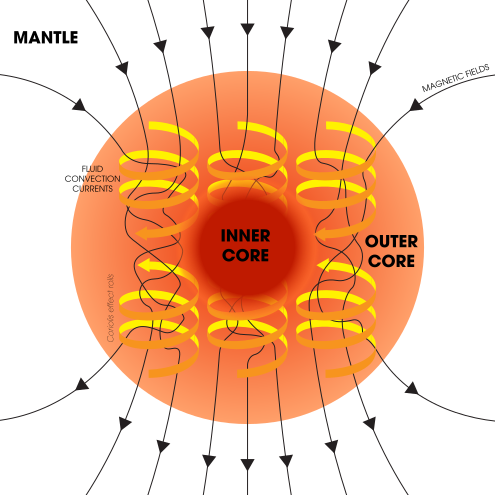
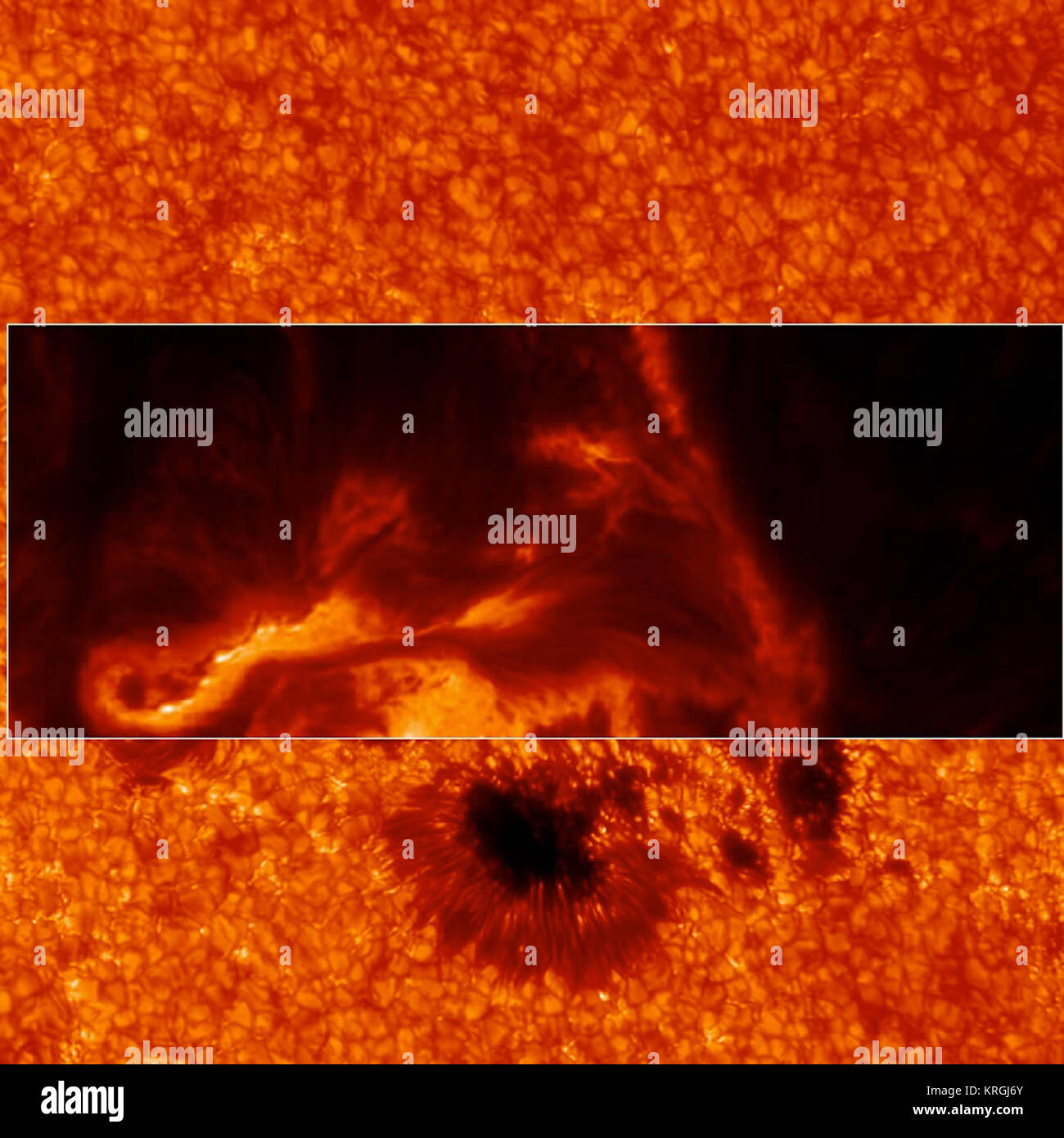
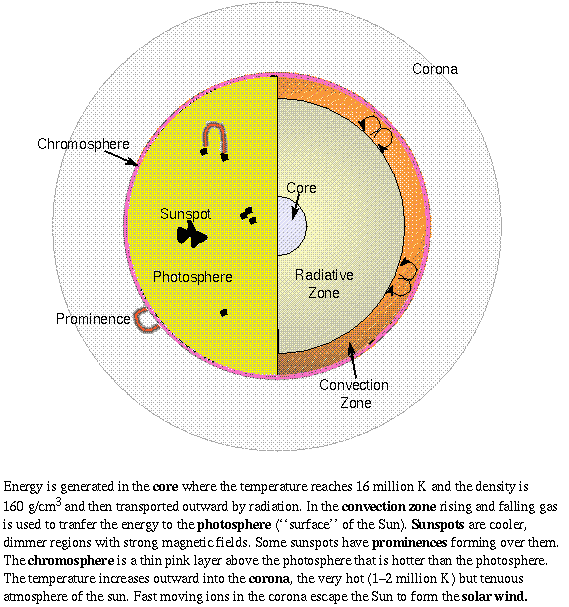
The Ocean Zones - WorldAtlas The sunlight zone, twilight zone, and deep ocean are the three major zones of the ocean. The deep ocean is further divided into 3 layers which are the midnight zone, the abyss and the trenches. The ocean covers more than 70% of the Earth's total surface and contains roughly 97% of all its water. Anatomy of the Sun | NASA The Chromosphere - This relatively thin layer of the Sun is sculpted by magnetic field lines that restrain the electrically charged solar plasma. Occasionally larger plasma features, called prominences, form and extend far into the very tenuous and hot corona, sometimes ejecting material away from the Sun.
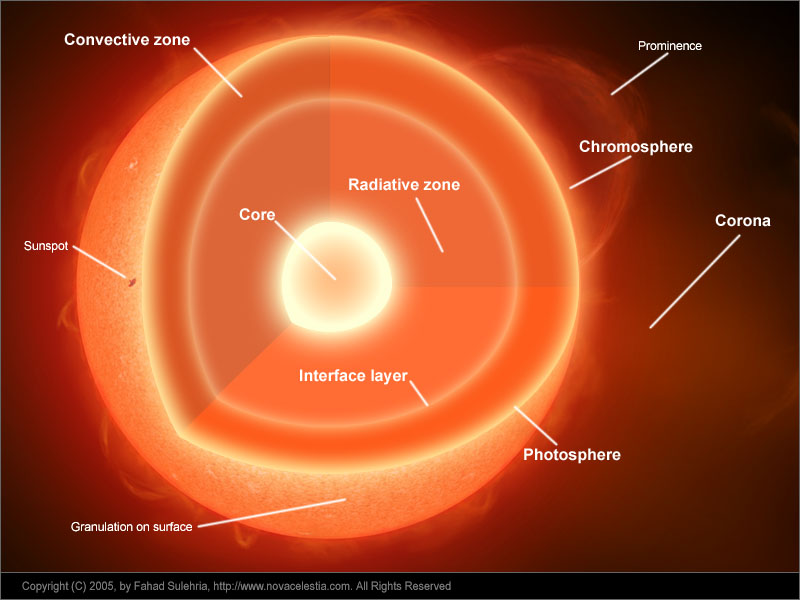
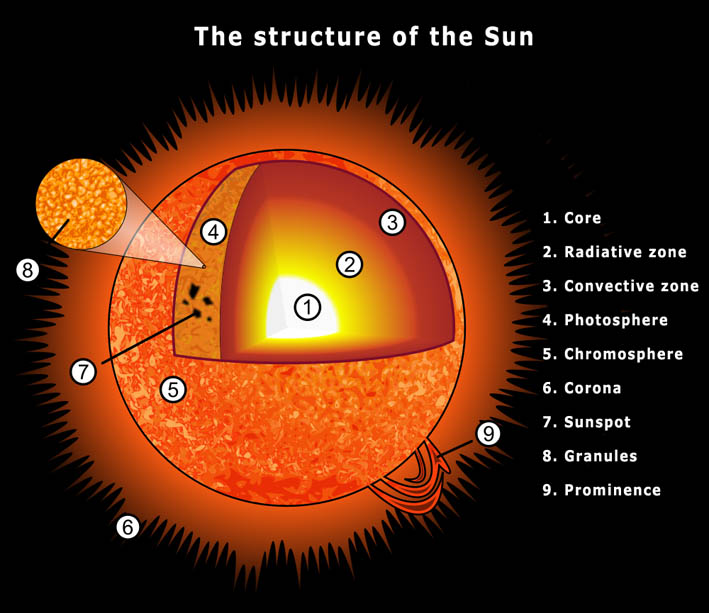
Anatomy of the Sun Diagram | Quizlet Radiative Zone It is the layer above the core. Energy produced in the core radiates through this layer, which is so dense that it takes more than 100,000 years (on average) for a photon to escape. Convection Zone Currents of plasma actively transport energy through this region.

Label the different areas of the sun.
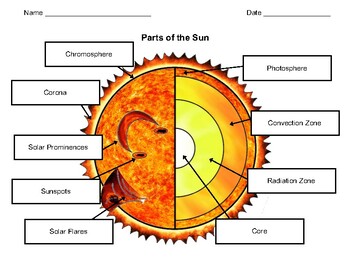
Earth-Sun Relationships | National Geographic Society Any circle drawn around the Earth divides it into two equal halves called hemispheres. There are generally considered to be four hemispheres: Northern, Southern, Eastern, and Western. Grades 6 - 12+ 48 encyclopedic entry Sun Astronomy, Biology, Earth Science, Physics Understand Your Garden's Sun and You'll Know What to Plant Where Sunlight, water, and soil are the key components for healthy foliage, flowers, and fruit. Of course, the amount of light your yard gets will change throughout the day as shadows from building and taller plants move with the sun. Most plants will thrive in at least six hours of direct sunlight, which for gardening purposes is called full sun. The Structure and Composition of the Sun | Astronomy | | Course Hero Parts of the Sun: This illustration shows the different parts of the Sun, from the hot core where the energy is generated through regions where energy is transported outward, first by radiation, then by convection, and then out through the solar atmosphere. The parts of the atmosphere are also labeled the photosphere, chromosphere, and corona.
Label the different areas of the sun.. Understanding Astronomy: The Sun and the Seasons The Arctic and Antarctic Circles mark the maximum reach of the sun's rays at the solstices. The Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn mark the locations where the rays of the noon sun are perpendicular to the ground at the solstices. (Earth image adapted from NASA data using John Walker's Earth and Moon Viewer .) Layers of the Sun - Science Facts Corona: The Outer Layer The outermost layer is the corona and can be seen during a solar eclipse when the sun is blocked by the moon. This layer is hotter than the surface of the sun. Less Than Five - Layers of the Sun Explained - Outer Layers Share Watch on The sun has many chemical elements but since it is so hot they are in a gaseous state. "Parts" of the Sun | Center for Science Education Scientists who study the Sun usually divide it up into three main regions: the Sun's interior, the solar atmosphere, and the visible "surface" of the Sun which lies between the interior and the atmosphere. There are three main parts to the Sun's interior: the core, the radiative zone, and the convective zone. The core is at the center. What Is the Sun's Role in Climate Change? The Sun powers life on Earth; it helps keep the planet warm enough for us to survive. It also influences Earth's climate: We know subtle changes in Earth's orbit around the Sun are responsible for the comings and goings of the past ice ages. But the warming we've seen over the last few decades is too rapid to be linked to changes in Earth ...
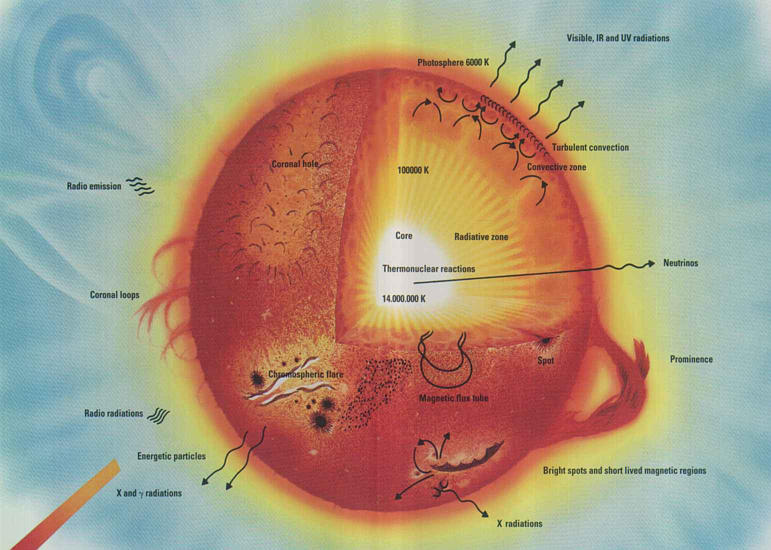
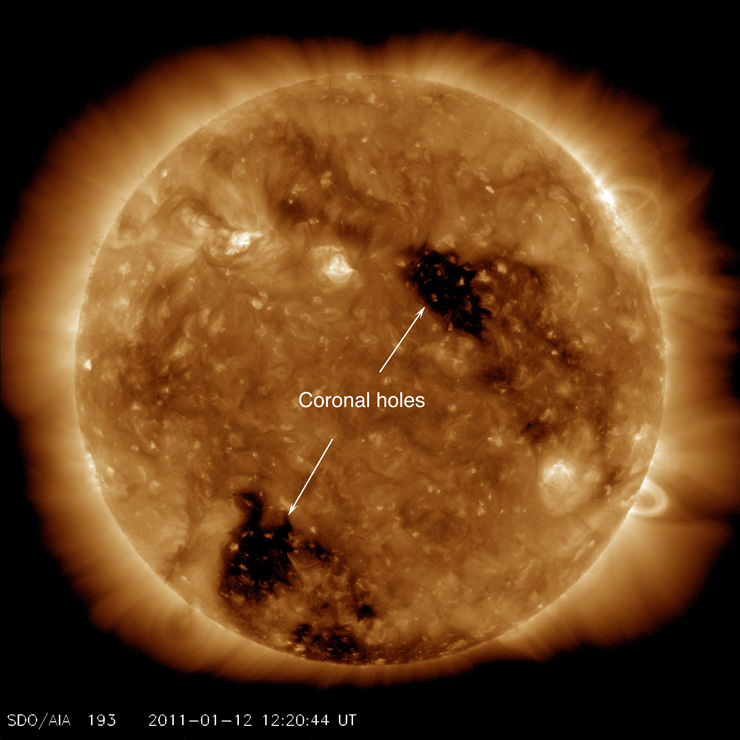
The Sun and Sunspots - National Weather Service Sunspots: One interesting aspect of the Sun is its sunspots. Sunspots are areas where the magnetic field is about 2,500 times stronger than Earth's, much higher than anywhere else on the Sun. Because of the strong magnetic field, the magnetic pressure increases while the surrounding atmospheric pressure decreases. Which statement describes the solar feature labeled A? Image of the sun ... A dark spot appearing from time to time on the sun's surface based on the description: "Image of the sun with three solar properties labeled by A, B, and C. Label A points to lit particles shooting outward from and then coming back towards the sun's surface. Label B points to a region on the sun's surface that is bright. Layers of the Sun | Parts of the Sun | DK Find Out At the very center is the dense, hot core. Around the core lie two layers: a thick layer called the radiative zone and a thinner, cooler layer called the convective zone. Surrounding all of them is the sun's surface layer, known as the photosphere. Above this lies the sun's thin atmosphere, which is made up of the chromosphere and the corona. Layers of the Sun | NASA Oct 10, 2012 · The inner layers are the Core, Radiative Zone and Convection Zone. The outer layers are the Photosphere, the Chromosphere, the Transition Region and the Corona. IRIS will focus its investigation on the Chromosphere and Transition Region. More detail on the outer layers follows:
What are the Parts of the Sun? - Universe Today Sep 13, 2016 · Photosphere: The layer of the Sun that we can see from Earth is called the photosphere. Below the photosphere, the Sun becomes opaque to visible light, and astronomers have to use other methods to... Parts of the Sun Flashcards | Quizlet Area on the Sun's surface that is cooler and less bright than surrounding areas is caused by the Sun's magnetic field and occur in cycles. Photosphere Lowest layer of the Sun's atmosphere; gives off light and has temperatures of about 6,000K. Chromosphere Layer of the Sun's atmosphere above the photosphere. Prominence PDF The Sun Worksheet - Northland Preparatory Academy Unlike Earth, the sun does not have a solid surface. Like Earth, the sun has an interior and an atmosphere. The sun's interior consists of the core, radiation zone, and convection zone. Each layer has different properties. The sun produces an enormous amount of energy in its core, or central region. The sun's energy comes from nuclear fusion. PDF Parts of the Sun - Solar Physics at MSU From the center out, the layers of the sun are as follows: the solar interior which is composed of the core, the radiative zone and the convective zone. The visible surface is made up of the photosphere and the chromosphere. The outermost layer is called the corona. In this lesson, students will learn about the sun, our closest star. Guidelines 1.
The Sun - Imagine the Universe! The three parts of the atmosphere, from the surface of the Sun outward are the photosphere, chromosphere, and corona. (Credit: NASA) The Photosphere Since the Sun is made up of hot gas, there isn't really a "surface" to it. Instead, as you move from space toward the Sun's core, the gas gets denser and denser.
How does the location of sunrise and sunset change throughout the year ... This marks the path of the Sun during summer solstice and the place where this circle cuts the horizons will mark the place where the Sun will rise and set on the day of summer solstice. A similar circle which is separated from the first circle by 23.5 degrees at zenith towards south will mark the path of the Sun on winter solstice.
In Depth | Sun - NASA Solar System Exploration Since the Sun is not solid, different parts rotate at different rates. At the equator, the Sun spins around once about every 25 Earth days, but at its poles, the Sun rotates once on its axis every 36 Earth days. Moons. As a star, the Sun doesn't have any moons, but the planets and their moons orbit the Sun. Rings. Rings
Sun - Internal structure | Britannica The energy radiated by the Sun is produced during the conversion of hydrogen (H) atoms to helium (He). The Sun is at least 90 percent hydrogen by number of atoms, so the fuel is readily available. Since one hydrogen atom weighs 1.0078 atomic mass units and a single helium atom weighs 4.0026, the conversion of four hydrogen atoms to one helium atom yields 0.0294 mass unit, which are all ...
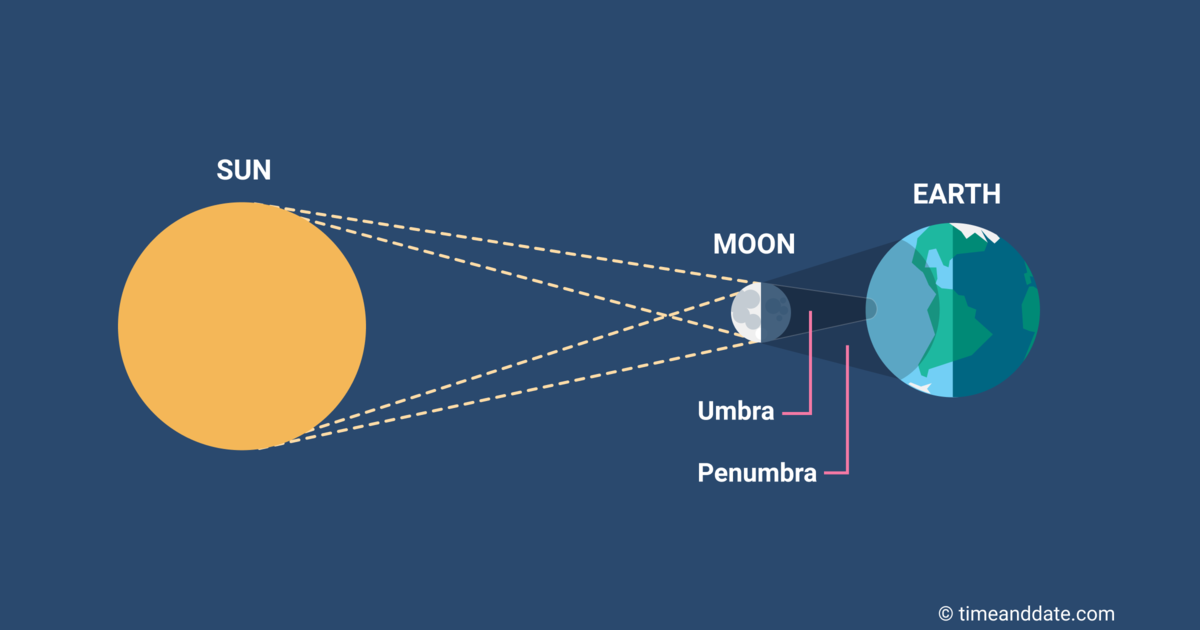
Eclipses of the Sun and Moon | Astronomy | | Course Hero One of the coincidences of living on Earth at the present time is that the two most prominent astronomical objects, the Sun and the Moon, have nearly the same apparent size in the sky.Although the Sun is about 400 times larger in diameter than the Moon, it is also about 400 times farther away, so both the Sun and the Moon have the same angular size—about 1/2°.
Layers of the Sun - The Sun Today with Dr. C. Alex Young From the center out, the layers of the Sun are as follows: the solar interior composed of the core (which occupies the innermost quarter or so of the Sun's radius), the radiative zone, and the convective zone, then there is the visible surface known as the photosphere, the chromosphere, and finally the outermost layer, the corona.
Surface Features of the Sun ( Read ) | Earth Science - CK-12 Foundation Describes the surface features of the Sun, including sunspots, solar prominences, solar flares, and coronal mass ejections. Quick Tips. Notes/Highlights.
Earth's rotation around the Sun and the sequence of four seasons The Earth revolves around the Sun once every 365 and quarter days (one year), The rotation of the Earth around the Sun causes the sequence of the four seasons (the summer - the spring - the autumn - the winter). The sequence of the four seasons. The Earth's axis is inclined and this causes the difference in the length of the day and the ...
Position of the Sun - Wikipedia To find the Sun's position for a given location at a given time, one may therefore proceed in three steps as follows: calculate the Sun's position in the ecliptic coordinate system, convert to the equatorial coordinate system, and convert to the horizontal coordinate system, for the observer's local time and location.
PDF All About that Tilt: Sun and Seasons - NASA activity to see how the angle of the Sun affects your shadow. For example, if you were standing at 45ºN latitude, the noon Sun angle at summer solstice would be: 45° N - 23.5° N = 21.5° 90° - 21.5° = 68.5° is the noon Sun angle . Find these Sun angles: Noon Sun angle at equinoxes. 45° N - 0° N = 45° 90° - 45° = ____° is the ...
Sun - Earth Relationship: The Seasons | Earth Science The seasons are caused by the direction Earth's axis is pointing relative to the Sun. The Earth revolves around the Sun once each year and spins on its axis of rotation once each day. This axis of rotation is tilted 23.5 degrees relative to its plane of orbit around the Sun. The axis of rotation is pointed toward Polaris, the North Star.
What Are The Layers Of The Sun? - WorldAtlas Jun 16, 2020 · The layers of the Sun are divided into two larger groups, the outer and the inner layers. The outer layers are the Corona, the Transition Region, the Chromosphere, and the Photosphere, while the inner layers are the Core, the Radiative Zone, and the Convection Zone. There are four outer layers of the Sun, and the Corona is the outermost one.
The Structure and Composition of the Sun | Astronomy | | Course Hero Parts of the Sun: This illustration shows the different parts of the Sun, from the hot core where the energy is generated through regions where energy is transported outward, first by radiation, then by convection, and then out through the solar atmosphere. The parts of the atmosphere are also labeled the photosphere, chromosphere, and corona.
Understand Your Garden's Sun and You'll Know What to Plant Where Sunlight, water, and soil are the key components for healthy foliage, flowers, and fruit. Of course, the amount of light your yard gets will change throughout the day as shadows from building and taller plants move with the sun. Most plants will thrive in at least six hours of direct sunlight, which for gardening purposes is called full sun.
Earth-Sun Relationships | National Geographic Society Any circle drawn around the Earth divides it into two equal halves called hemispheres. There are generally considered to be four hemispheres: Northern, Southern, Eastern, and Western. Grades 6 - 12+ 48 encyclopedic entry Sun Astronomy, Biology, Earth Science, Physics




















Post a Comment for "40 label the different areas of the sun."