43 label the structures of the thoracic cavity.
qualifications.pearson.com › content › damUnit 1: Principles of Anatomy and Physiology in Sport - Edexcel Major muscles: diagrams and sticky label game Assignment 2: The Muscular System (P3, P4, M1, D1). Tutor introduces the assignment brief Fibre types and characteristics of each: learner-centred research Antagonistic pairs and different types of muscle contraction – practical session Structure of the heart – theory and practical dissection Label the structures of the thoracic cavity - ForNoob Label the structures of the thoracic cavity Parietal pleura Parietal pleura Pleural cavity Visceral pleura Visceral pleura The pericardium is a membranous sac around the heart and as two layers that is the outer fibrous pericardium and inner serous pericardium. The inner serous pericardium has two thin layers that are the parietal pericardium ...
› Thoracic_ExaminationThoracic Examination - Physiopedia The examiners observe the patient’s thoracic spine region and assess for the presence of deviation from normal including the thoracic spine curvatures in the frontal and sagittal planes. The overall impression of inter-rater reliability for postural observation of kyphosis and label either excessive, normal or decrease range from moderate to ...
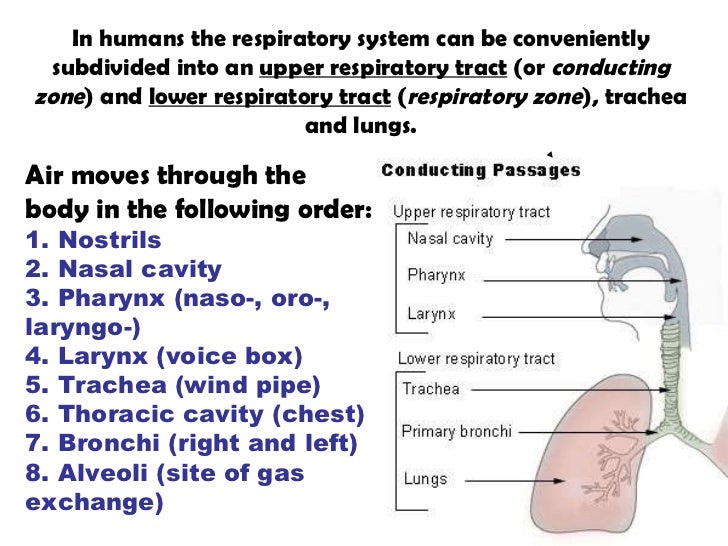
Label the structures of the thoracic cavity.
(Get Answer) - Label the structures of the thoracic cavity.. Label the ... Label the structures of the thoracic cavity. a table-tennis ball is thrown at stationary bowling ball makes one-dimensional elastic collision and bounce back along the same line. compared with the bowling ball after the collision, does the table have a) larger magnitude of momentum and more... Label the structures of the thoracic cavity - Soetrust Please describe the thoracic cavity. Please name the organs…. which body cavity affords the least protection to its…. Can you label the structures of a plant cell? Label the structures of the ankle and foot. Limb bones within unrelated animals that have the same basic…. Analyze the RTE breakfast cereal industry. Thoracic Cavity - Introduction, Structure, Organs, and FAQs In the centre of the chest between the lungs is the mediastinum that comprises the organs that are located inside it. Structures within the thoracic cavity include: Oesophagus of the digestive system Thymus gland Vagus nerve and parasympathetic veins. Diaphragm, trachea, bronchi, lungs. The heart The superior and inferior vena cava.
Label the structures of the thoracic cavity.. Thoracic Anatomy - Physiopedia The ribs are the bony framework of the thoracic cavity. The ribs form the main structure of the thoracic cage protecting the thoracic organs, however their main function is to aid respiration. There are twelve pairs of ribs. Each rib articulates posteriorly with two thoracic vertebrae by the costovertebral joint. Solved Label the structures of the thoracic cavity. Trachea | Chegg.com Anatomy and Physiology. Anatomy and Physiology questions and answers. Label the structures of the thoracic cavity. Trachea Diaphragm Esophagus. Question: Label the structures of the thoracic cavity. Trachea Diaphragm Esophagus. Body Cavities - Simple Anatomy and Physiology The thoracic cavity and abdominopelvic cavity are separated by the diaphragm, which is a thin skeletal muscle. Thoracic cavity: located in the chest (upper part of the trunk) and contains the heart and the lungs. The thoracic cavity is subdivided into smaller cavities. The right pleural cavity contains the right lung, and the left pleural ... Label the thoracic cavities.docx - Label the cavities below; Answer the ... In the figure above - locate the thoracic cavity. Labelthe structure that separatesthe thoracic cavity from the abdominopelvic cavity Notice the 4 colors of the thoracic cavity. There are two purple cavities within the thoracic cavity. Labelthem. Identifythe two / three primary structures that lie within the purple cavity. Notice the green cavity.
Thoracic cage: Anatomy and clinical notes | Kenhub The thoracic cage (rib cage) is the skeleton of the thoracic wall. It is formed by the 12 thoracic vertebrae, 12 pairs of ribs and associated costal cartilages and the sternum . The thoracic cage takes the form of a domed bird cage with the horizontal bars formed by ribs and costal cartilages. It is supported by the vertical sternum (anteriorly ... Anatomy, Thorax, Muscles - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf The thoracic wall is made up of five muscles: the external intercostal muscles, internal intercostal muscles, innermost intercostal muscles, subcostalis, and transversus thoracis. These muscles are primarily responsible for changing the volume of the thoracic cavity during respiration. Other muscles that do not make up the thoracic wall, but attach to it include the pectoralis major and minor ... Thoracic Cavity - Anatomy | Organs | Functions | 8 Types of Cavities Thoracic Cavity Right and left serous membrane cavities (contain right and left lungs) Mediastinum: Higher portion stuffed with blood vessels, trachea, esophagus, and thymus. The lower portion contains pericardial space (the heart is found at intervals the serosa cavity) 3. Serous Membranes Line of body cavities and canopy organs. Consist of Pre-Lab Exercise 16-2 Anatomy of the Thoracic Cavity Label and color ... Pre-Lab Exercise 16-2 Anatomy of the Thoracic Cavity Label and color the structures in the thoracic cavity in Fig text and Exercise 16-1 in this unit for reference 16with the terms from Excise 16-161931. Use your FIGURE 16.1 The thoracic cavity Cardiovascular System-Part1: The Heart I UNIT 16 Pre-Lab Exercise 16-3 Anatomy of the Heart Label and color the three views of the heart in Figure 16.2 ...
Anatomy Exam 4 Flashcards | Quizlet Correctly label the following areas of the thoracic cavity in the newborn and adult Which pancreatic cells secrete insulin beta cells what makes a cell responsive to a particular hormone the presence of a receptor for that particular hormone Which of the following glands has more exocrine than endocrine tissue the pancreas The Thoracic Cage: Bones, Structure & Classifications - Study.com The Thoracic Cage. The bony framework of the chest known as the human rib cage is also called the thoracic cage. This structure serves a very important purpose: to protect our vital organs such as ... teachmeanatomy.infoTeachMeAnatomy - Making Anatomy Simple Containing over 700 vibrant, full-colour images, TeachMeAnatomy is a comprehensive anatomy encyclopedia presented in a visually-appealing, easy-to-read format. Organs in the Thoracic Cavity - Bodytomy The thoracic cavity is lined by a serous membrane that exudes a thin fluid (serum). The chest membrane, also known as parietal pleura, extends further to cover the lungs. This part of the membrane is known as the visceral pleura. The part of the membrane that covers the heart, esophagus, and the great vessels is known as mediastinal pleura.
The Thoracic Cage - Anatomy and Physiology Thoracic Cage. The thoracic cage is formed by the (a) sternum and (b) 12 pairs of ribs with their costal cartilages. The ribs are anchored posteriorly to the 12 thoracic vertebrae. The sternum consists of the manubrium, body, and xiphoid process. The ribs are classified as true ribs (1-7) and false ribs (8-12).
Body Cavities and Membranes: Labeled Diagram, Definitions First, the cranium/skull is on the outside which encloses the cranial cavity. Below the skull is 3 layers of membrane called the meninges. The 3 meningeal layers are labeled with the stars. The outermost layer of the meninges is the dura mater, which is located beneath the skull.
Anatomy: Thoracic Cavity - RnCeus.com The thoracic cavity is made up of 12 pairs of ribs that connect in the posterior thorax to the vertebral bodies of the spinal column. In the anterior thorax, the first 7 pairs of ribs are attached to the sternum or breastbone by cartilage. ... Please review the important landmarks of the bony thoracic anatomy. The following diagram shows the ...
thoracic cavity | Description, Anatomy, & Physiology | Britannica thoracic cavity, also called chest cavity, the second largest hollow space of the body. It is enclosed by the ribs, the vertebral column, and the sternum, or breastbone, and is separated from the abdominal cavity (the body's largest hollow space) by a muscular and membranous partition, the diaphragm.
Thoracic Cavity - Definition & Organs of Chest Cavity | Biology Dictionary The thoracic cavity is actually composed of three spaces each lined with mesothelium, a special film-like tissue that separates vital organs. The pleural cavities surround the lungs, while the pericardial cavity surrounds and protects the heart. These tissues in the thoracic cavity can be seen in the image below.
Anatomy, Thorax - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf The thorax is the region between the abdomen inferiorly and the root of the neck superiorly.[1][2] It forms from the thoracic wall, its superficial structures (breast, muscles, and skin) and the thoracic cavity. An official website of the United States government Here's how you know The .gov means it's official.
quizlet.com › 511891167 › bio-232-lab-midterm-flashBio 232 ~ Lab Midterm Flashcards | Quizlet Drag each label into the proper position to identify the correct cavity. ... Label the structures of a typical thoracic vertebra. Label the structures of the vertebra.
Answered: Correctly label the muscles of the… | bartleby Transcribed Image Text: Correctly label the muscles of the thoracic cavity and the abdomen. 3. Transverse abdominal (cut) 02:21:37 Internal oblique (cut) External intercostals Internal intercostals Pectoralis minor Pectoralis minor Internal abdominal oblique Serratus anterior External intercostals Internal intercostals Rectus sheath Rectus sheath Postenor wal of rectus sheath (rectus abdominis ...


Post a Comment for "43 label the structures of the thoracic cavity."